
Important Security Alert: Issue Found in React (Common Website Technology)
A serious security fault has been discovered in a piece of software called React, which many websites and online services use behind the scenes. This…
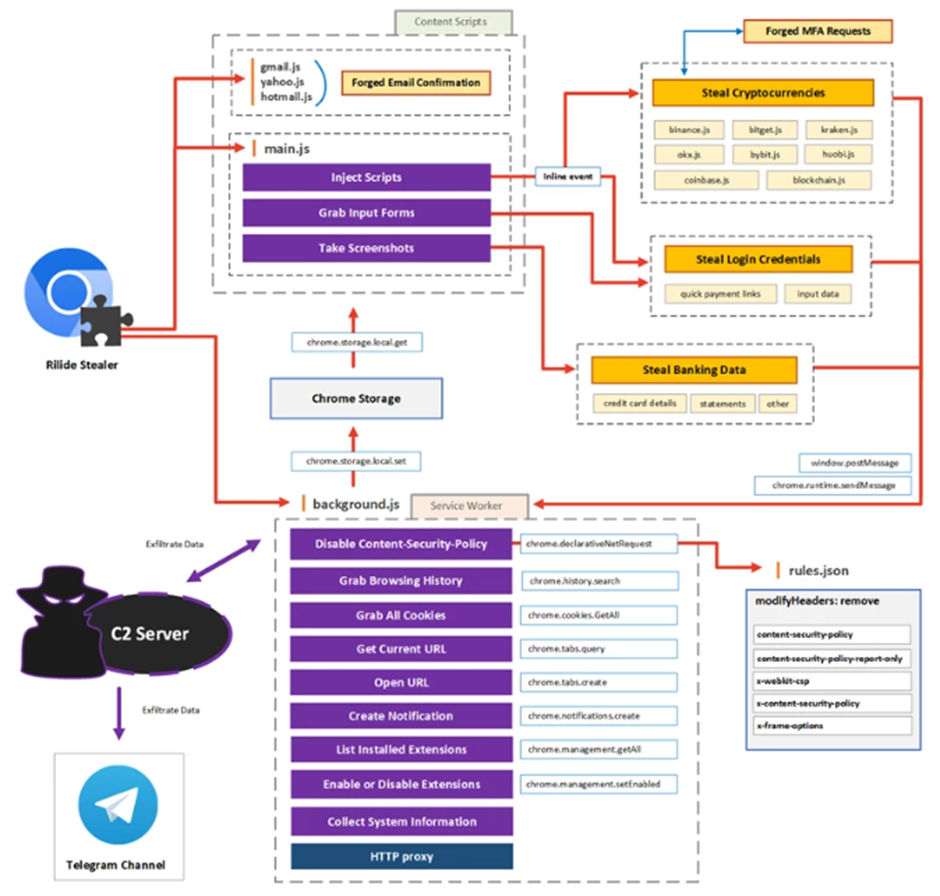
A new iteration of the Rilide Stealer has surfaced, focusing its efforts on web browsers such as Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Brave, and Opera. Its primary objective remains the illicit acquisition of sensitive information and cryptocurrencies. This updated version bears striking similarities to the CookieGenesis malware.
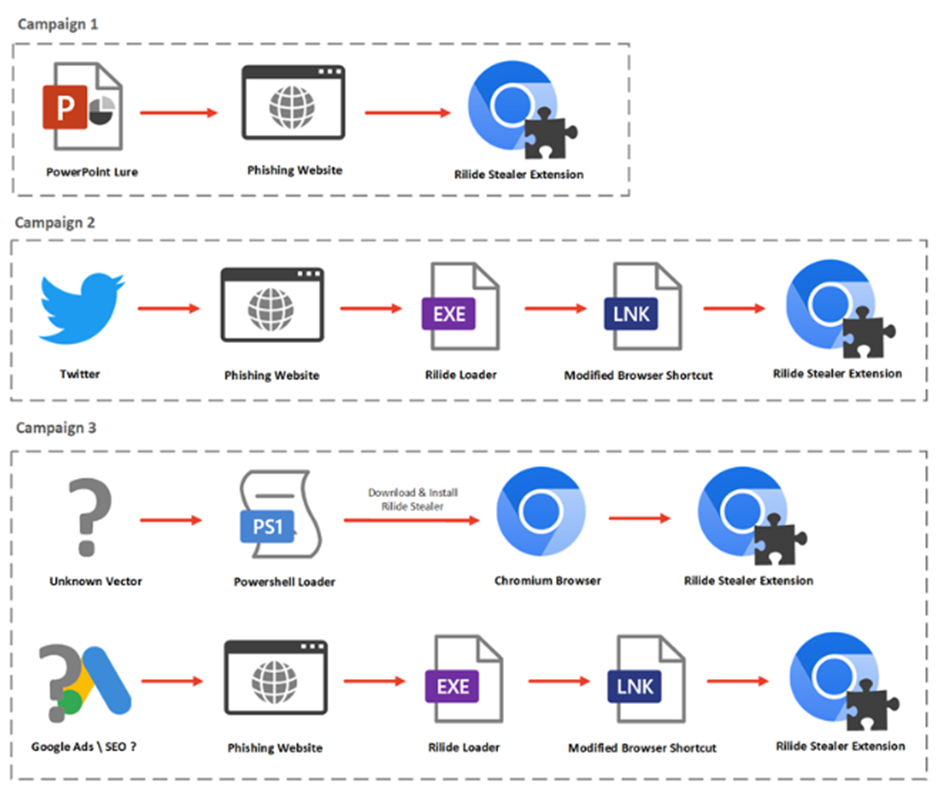
Trustwave researchers have detected instances of these malicious activities occurring online. They have identified over 1,300 phishing websites distributing this fresh variant of Rilide Stealer, often accompanied by other harmful malware such as Bumblebee, IcedID, and Phorpiex. These deceptive websites masquerade as various entities, ranging from banks and government services to software firms, delivery services, and even crypto token giveaways.
The strategies employed by these campaigns exhibit diversity. In one case, attackers used a PowerPoint document trick to entice victims, along with a counterfeit Palo Alto GlobalProtect plugin designed for corporate users. In another instance, a fabricated “Play-to-Earn” (P2E) game installer, promoted through Twitter, was exploited to deliver Rilide and Redline Stealer. Yet another scheme targeted banking users in Australia and the U.K., employing AngelDrainer scripts to siphon cryptocurrencies from wallets.
Noteworthy advancements have been made in the malware’s evolution. While resembling its April-identified predecessor, the latest version of Rilide demonstrates increased complexity due to code obfuscation and alignment with the Chrome Extension Manifest V3. A newly introduced command named ‘screenshot_rules’ empowers attackers to capture screenshots of active tabs periodically. Additionally, this version can transmit stolen data, including credit card details, to a Telegram channel.
Of significant concern is the leaked source code for the Rilide extension in February. This raises the possibility that threat actors beyond the initial group might have taken up its development. Consequently, organizations are strongly advised to employ Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) and comprehend the nature and scope of attacks carried out by this latest version. Such understanding is pivotal for implementing the required security measures.