
Important Security Alert: Issue Found in React (Common Website Technology)
A serious security fault has been discovered in a piece of software called React, which many websites and online services use behind the scenes. This…
Current cyber security incidents involving SaaS platforms, such as Midnight Blizzard targeting Microsoft and the Cloudflare-Atlassian breach, have outlined the vital significance of safeguarding personal data within cloud environments. These incidents have not only raised alerts about the vulnerabilities in SaaS platforms but have also highlighted the elaborate security challenges faced by organisations in preserving their systems.
Threat actors manipulated various vulnerabilities to acquire unauthorised access. The Midnight Blizzard attack used password spraying to breach legacy accounts that did not utilise multi-factor authentication (MFA), letting attackers access OAuth apps with high-level permissions and office communications. Likewise, the Cloudflare-Atlassian breach originated from compromised user information received from a previous breach, allowing hackers to access internal systems, and possibly extract essential source code repositories.
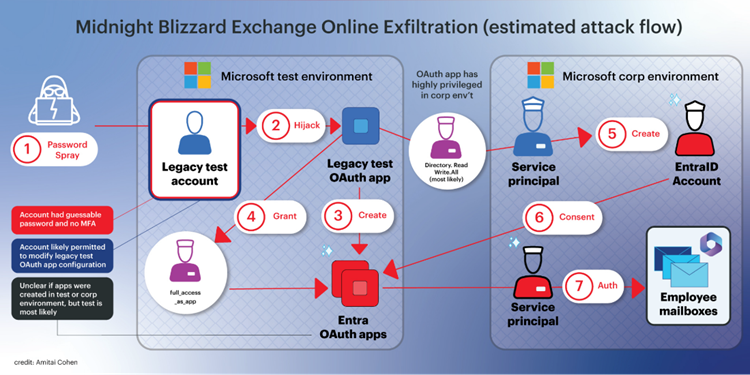
These incidents underscore the vital importance of continuous vigilance in overseeing SaaS ecosystems, spotlighting the relentless risk posed by sophisticated cyber adversaries targeting essential infrastructure and the technological foundations underpinning operations. Furthermore, these breaches draw attention to the acute vulnerabilities in managing identities within SaaS platforms and the urgent requirement for robust risk management protocols for third-party applications.
Attackers deploy standardised tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) in their strategy to infiltrate SaaS providers, utilising a structured approach known as the kill chain:
Initial Access: Employing techniques such as password spraying and OAuth hijacking.
Persistence: Masquerading as administrators and generating additional OAuth credentials.
Defence Evasion: Utilising OAuth with high privileges and bypassing multi-factor authentication (MFA).
Lateral Movement: Achieving a wider compromise of interconnected applications.
Data Exfiltration: Extracting sensitive and privileged information from applications.
To decrease the threats associated with SaaS exploits, businesses must take assertive actions:
As organisations increasingly depend on SaaS platforms for their tasks, it is crucial to manage vulnerabilities and security problems affiliated with cloud environments. By implementing robust security standards, staying vigilant against evolving threats, and capitalising on cutting-edge security solutions, institutions can effectively eliminate the threats posed by SaaS exposures and safeguard their sensitive data.