
Data Privacy Starts With Cyber Basics
Data Privacy Day is a useful reminder that privacy and cyber security are not separate conversations. You can have the best privacy policy in the…
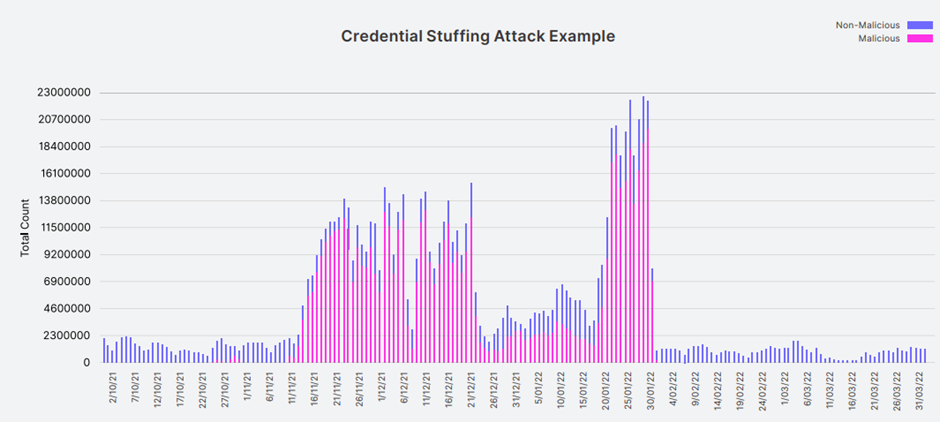
If you’ve ever had an account on a website affected by a data breach, then chances are your credentials may be used in credential-stuffing attacks. These attacks are increasing, with multi-factor authentication company Okta reporting that they detected almost 10 billion credential-stuffing login attempts on their platform in the first 90 days of 2022.
Credential stuffing attacks are a form of cyber attack that involves taking credentials found in data breaches and using them to attempt to log in to accounts on other sites. These attacks occur as people often reuse username and password combinations for multiple online accounts.
A recent rise in credential stuffing attacks may be due to an increase in the availability of botnets which are vast networks of compromised devices used by hackers to perform malicious activity. To perform credential stuffing attacks, hackers obtain large lists of login details (often bought on the dark web) and give the details to bots, which then attempt to log in to a website of the hacker’s choice.
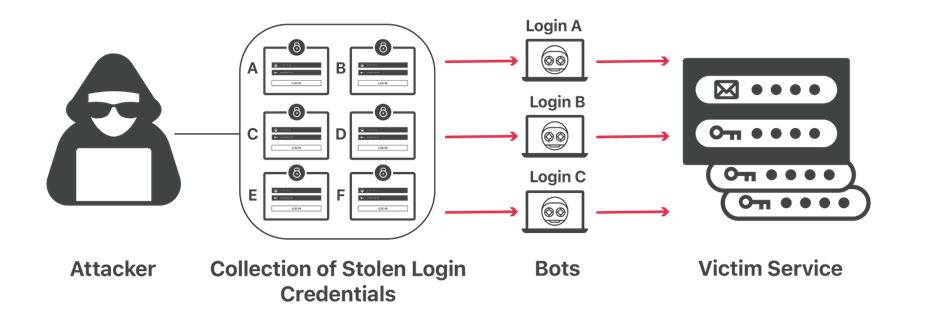
The aim of credential stuffing attacks is typically to obtain sensitive information the hacker can financially gain from. Websites that hold users’ banking details are highly targeted; however, hackers will also target sites that hold information which could be used in phishing attacks.
When sites are targeted with credential stuffing attacks, it is not only the user’s accounts that are affected but also the website’s technology. These attacks typically increase activity, with the targeted site responding to malicious internet traffic and regular traffic from legitimate users. Because of this, credential stuffing attacks can cause a site to start significantly lagging or even crash during an attack.
For individual users, preventing credential stuffing attacks from becoming successful is as simple as using a different password for every account you create. Each password should be unique and not slightly changed from another password. The best way to create unique passwords is by using three random words alongside numbers and special characters.
Understandably, remembering a new password for every account can be incredibly difficult. To help with this, consider using a password manager. Password managers are safe and secure applications that store your username and password combinations.
Additionally, setting up multi-factor authentication (MFA) can help boost your account’s security. Most large organisations support MFA, and setting it up can typically be done quickly within your account’s settings.
Sites like https://haveibeenpwned.com/ can show you if any accounts linked to your email have been involved in a data breach. If so, it is best to change the password on your affected accounts to be safe.
A credential stuffing attack can target any website with a login feature. However, this form of cyber attack notably targets users, not the organisation running the site, and originates from other organisations suffering data breaches. However, a company victimised by these attacks may still face backlash for allowing the accounts to be compromised in this way.
To prevent a credential stuffing attack from happening to your website, you can use login methods that make it difficult for bots to perform login attempts. Think about using features such as reCAPTCHA, a program that can distinguish between a genuine user and a bot user by making the user click on a button to confirm they are not robots. Additionally, making all users log in with MFA can prevent any accounts from being compromised; however, it may not stop the traffic from a credential-stuffing attack affecting your site’s performance.
There are also numerous ways to help you detect real users from bots through data created when a user interacts with your website. Methods such as device fingerprinting can show the stark difference between traffic made by a human login vs a bot login and can be used to filter out traffic that doesn’t originate from real users.
Sometimes, more minor credential-stuffing attacks will originate from a very small pool of IP addresses. If you notice a small number of IP addresses creating a considerable amount of traffic, consider making an IP block list to prevent the device at that address from targeting you.